
Seismic Volatility Reshapes SEO Landscape as AI Overviews Expand & Authenticity Becomes Non-Negotiable
When Google announced its December 2025 core update on December 11, the language was familiar: “a regular update designed to better surface relevant, satisfying content for searchers.” But what unfolded over the next 18 days was anything but regular. By December 29, when the rollout was completed, SEMrush’s volatility sensor had hit 8.7 out of 10—the highest reading recorded in all of 2025. For context: the previous year’s worst month (June’s core update) peaked at 8.1.
What made December different wasn’t just the intensity. It was what the volatility revealed about Google’s priorities—and how brutally the algorithm enforced them.
Between 40% and 60% of websites globally experienced measurable ranking changes. E-commerce sites reported a 52% impact rate, health and YMYL sites saw 67% affected, and affiliate sites were hammered hardest: 71% reported negative traffic impacts. But the December earthquake wasn’t isolated. It arrived alongside two other signals that collectively rewrote the SEO rulebook.
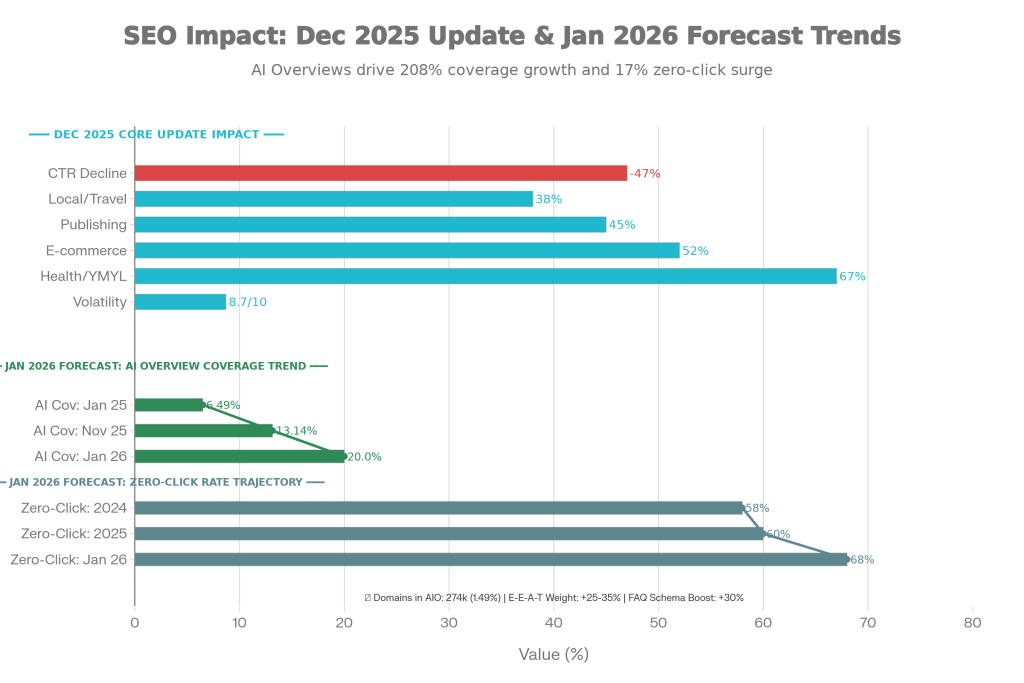
Google expanded monetized ads inside AI Overviews to 11+ countries on December 19, including India. This marked the moment when Google formally converted AI summaries from a free feature into a paid channel. With AI Overviews now triggering on 13.14% of all queries (up 102% from January 2025’s 6.49%), organic CTR has collapsed to 8% when AIOs appear versus 15% without them—a 47% decline. Worse: only 1% of users click the cited sources directly, meaning that organic visibility alone is increasingly worthless for commercial intent.
On December 19, Google’s Senior Search Analyst endorsed a critical article on Bluesky, calling most SEO content “digital mulch” designed to “fill space, hit metrics, and appease the gods of Google.” This wasn’t Mueller being provocative; it was an official signal timed precisely during the core update’s rollout—and it aligned perfectly with observed SERP patterns.
Together, these three signals told a coherent story: Ranking positions are becoming irrelevant. Being cited by AI matters. And writing for algorithms instead of humans is now algorithmically penalized.
One of the December update’s cruelest surprises was its selective targeting of winners from previous updates.
Glenn Gabe, a respected SERP analyst, noted in his December analysis that many sites that gained visibility in November’s more benign update saw those gains completely reverse in December. The update didn’t just reshuffle the deck; it dealt from a different deck entirely.
This created a whip-lash effect for practitioners. A site that had spent three weeks optimizing for November’s signals—and saw 20-30% traffic recovery—suddenly lost 40-50% in December. The frustration in SEO forums was palpable. One affiliate site operator reported: “We optimized for the November recovery. December punished us for it.”
The pattern suggests Google’s ranking systems are more fragmented than ever. Instead of one cohesive algorithm, Google appears to be running multiple, sometimes contradictory ranking systems simultaneously. As Lily Ray noted, this fragmentation explains why different sites respond differently to the same update, and why previous recovery strategies may not apply.
Affiliate marketing faced near-extinction in December. A typical pattern: an affiliate site with 150 product review pages saw 90% traffic loss on pages created through pure research and aggregation, while pages where the owner actually tested products for 2-3 weeks maintained rankings.
The differentiation was stark. Google’s algorithm now clearly distinguishes between:
One affected operator summed it up: “The era of affiliate sites ranking through SEO optimization alone has ended.”
E-commerce wasn’t hit uniformly. Instead, the update applied quality within category:
The lesson: commoditized product content is now worthless. Originality and genuine expertise are the only moats.
When an AI Overview appears (which happens on ~94% of fashion queries), the first traditional organic listing is pushed down 1,718 pixels—past outfit recommendations, styling tips, and multi-source links. E-commerce sites are learning that traditional organic traffic is no longer the primary channel.
The health sector revealed the starkest expertise gaps:
Winners:
Losers:
This wasn’t subtle. Google’s algorithm is now evaluating whether the author is qualified to speak on health topics, not just whether the content matches intent. A well-written wellness article by a non-medical influencer lost 67% traffic. A mediocre article by a hospital lost nothing.
Major news publishers saw massive volatility. But recovery patterns were clear:
Winners had: original reporting, clear bylines with author backgrounds, documented editorial standards, and transparent ownership/funding.
Losers had: news aggregation, clickbait headlines, unclear ownership, and known accuracy issues.
One publisher reported a 98% drop in Discover impressions during the update window, hitting when December ad rates were at their peak—the worst possible timing.
E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) isn’t new. But December marked a quantum leap in how Google operationalizes it.
Previously, E-E-A-T signals were most critical for YMYL topics. As of December 2025, Google now applies enhanced E-E-A-T evaluation across all content types—including entertainment, lifestyle, and tech.
What changed:
The result: Single-page optimization is dead. You’re now ranked as an entity—an author, a brand, a domain—across your entire digital presence.
In previous updates, excellent Core Web Vitals were a competitive advantage. As of December 2025, they’re a qualification gate.
Sites with poor performance metrics experienced 20-30% worse traffic losses than faster competitors with equivalent content quality.
Specific findings:
One site operator reported fixing mobile experience issues resulted in 15% traffic recovery within three weeks—despite making zero content changes. This demonstrates that technical optimization can meaningfully counteract content-quality issues.
One of December’s most misunderstood aspects: Google didn’t penalize AI usage. It penalized low-effort AI.
What the data showed:
Google’s algorithm can now detect which content was created primarily for ranking vs. created for users. Mass-produced AI roundups lost 87-88% of traffic. But a subject matter expert using AI to accelerate research and editing? Those sites saw minimal to positive impact.
Industry leaders are increasingly framing 2026 as the year of GEO—Generative Engine Optimization—instead of traditional SEO.
Duane Martinez, a strategic SEO analyst, argues that the December update marks the formal inflection point. “SEO was optimizing for ranking. GEO is optimizing for citation visibility in AI systems, entity authority across platforms, and demonstrable expertise,” he wrote in a December analysis.
This shift has practical implications:
Zero-click traffic is accelerating. With AI Overviews expanding and citations creating only 1% click-through rates, organic traffic as a metric is approaching obsolescence. Alternative metrics—brand mentions, citations, sharing—are becoming primary.
Sites that are recovering fastest follow a clear pattern:
Week 1-2: Identify losers vs. winners. Reverse-engineer winners for shared characteristics (author credentials, content depth, Core Web Vitals, freshness signals). Apply 80/20 fixes to top losers: add author bios, remove preamble/filler, fix mobile Core Web Vitals.
Week 3-4: Strengthen entity authority. Link author bios to LinkedIn/credentials. Create a “What Is [Topic]?” hub page. Add Person and Organization schema. Implement FAQ schema for extractability.
Ongoing: Monitor AIO citation patterns. Track whether your domain appears in AI Overviews for target queries. Optimize top-cited pages for further visibility. Build “citation-native” content designed for AI extraction.
A case study by Manja, a service provider site, achieved 45% traffic recovery in 2 weeks by focusing on E-E-A-T strengthening, Core Web Vitals optimization, and backlink cleanup. Another site, in the automotive services space, recovered from 100 organic clicks/day (after being devastated by 2023 updates) to 400-500 clicks/day, but required 14+ months of systematic changes.
The timeline matters: most sites see meaningful recovery in 2-6 months; full recovery typically takes 6-12 months. But early action (within weeks, not months) correlates strongly with faster recovery.
December 2025 wasn’t a typical core update. It was Google’s most explicit statement yet about where search is heading:
For practitioners, the message is stark: optimize for being cited by AI, not for ranking in organic results. Build demonstrable expertise. Stop writing for algorithms. Fix technical fundamentals. And understand that your competition isn’t other websites anymore—it’s AI systems deciding whether to cite you at all.
The SEOs who adapt to this shift in January will thrive in 2026. Those who wait will be competing for the crumbs left over after AI takes the meal.
Stay ahead of Google updates, AI search experiments, and SEO automation workflows with insights from global top SEO minds. No noise - just what matters, delivered every week.